Inflammation is like your body’s fire alarm, signaling that something might be wrong. When you face threats like infections or injuries, your immune system kicks into gear. Blood vessels release plasma and white blood cells into the affected areas, which helps start the healing process and fight off any harmful invaders.
However, inflammation can be tricky. While short-term, or acute, inflammation is necessary for recovery, long-term, or chronic, inflammation can go unnoticed and lead to various health problems such as arthritis and heart disease.
Understanding what causes inflammation, its effects, and how to manage it is important for staying healthy and preventing future issues.
Inflammation is your body’s natural defense system responding to damage or stress. It comes in two forms: acute and chronic. Each type has different characteristics and impacts on health.
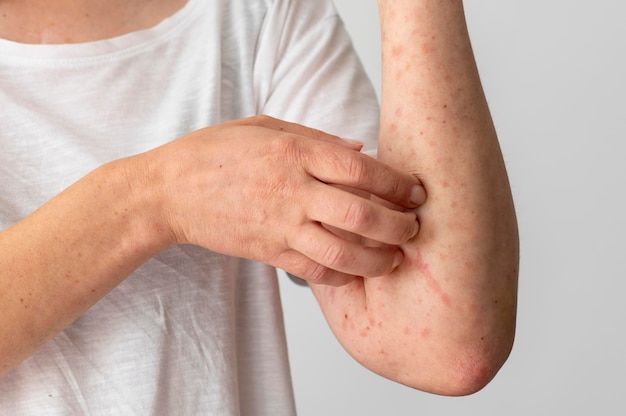
Acute inflammation is your body’s immediate reaction to injury or infection—like when you cut your finger, twist your ankle, or catch a cold. Your immune system sends white blood cells to the affected area to protect it and start healing. Typical signs of acute inflammation include redness, swelling, and pain. Normally, this type of inflammation resolves quickly as you heal, making it an essential part of your body’s defense.
Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is more subtle and can be damaging over time. Unlike acute inflammation, which goes away after completing its protective role, chronic inflammation can last for months or even years, often without noticeable symptoms. This prolonged state of alert can wear down the body, leading to various diseases. Chronic inflammation is often linked to serious health conditions like diabetes, cancer, and heart disease.
Detecting chronic inflammation usually involves blood tests that look for markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), which is produced by the liver in response to inflammation. High levels of CRP often indicate an inflammatory process somewhere in the body.
Managing chronic inflammation needs a comprehensive approach involving lifestyle changes, diet adjustments, and sometimes medication. Recognizing and addressing inflammation early can prevent it from developing into a chronic, disease-promoting state.
To control inflammation, adopt a holistic approach.